Inhale. Exhale. Breathing is the rhythm of life, alongside the heart’s backbeat.
Oxygen is required for life to exist. This component of Earth’s atmosphere, which helps to sustain life, makes up 20 percent of it and 65% of your body weight.
Serious health problems may occur when your body lacks oxygen.
When you breathe in, you’re breathing in oxygen. Oxygen links to your red blood cells after passing through your lungs.
Your blood then transports oxygen to every cell in your body via your circulatory system.
Cells rely on oxygen molecules for energy and maintenance.
The cells die if they are deprived of oxygen, and your organs shut down.
What is hypoxemia?
It is critical to have the right amount of oxygen in your blood.
Too little or too much oxygen is detrimental to one’s health. As a result, your body maintains and manages the proportion of oxygen in your circulation at all times.
When your body is unable to do so, owing to a lack of capability on its part, the condition is called hypoxemia.
What is the cause of hypoxemia?
Hypoxemia can be caused by a variety of issues and circumstances, including:
- Heart and breathing problems include Heart conditions, such as congenital heart defects or acquired heart diseases like cardiomyopathy.
- Breathing difficulties caused by asthma, emphysema, and bronchitis are other examples of lung issues that can be prevented through proper nursing care.
- High-altitude locations where oxygen levels in the air are lower are also a common cause of hypoxemia.
- Less commonly, hypoxemia can be caused by problems with the kidneys or liver that interfere with the production of red blood cells. Finally, toxic gases or fumes can also lead to hypoxemia.
What are the symptoms of hypoxemia?
The signs of hypoxemia differ depending on the degree of disease. They are as follows:
- Headache,
- fast heartbeat,
- shortness of breath, and
- Coughing is all possible symptom. Coughing is a common symptom. Confusion is another typical occurrence.
- Bluish discoloration of the skin, fingernails, and lips is also a possibility if hypoxemia is prolonged or severe.
- Children may also develop complications in the form of behavioral issues in cases of serious oxygen deprivation.
What is the oxygen level in the blood?

Normal blood oxygen levels range from 95 to 100 millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
Levels below 90 mmHg are considered low and can cause health problems.
Levels below 70 mmHg can be life-threatening.
Your body’s cells need oxygen
Hypoxia may reduce the amount of oxygen your body receives.
Hypoxia occurs when tissues and organs in your body don’t get enough oxygen to operate properly.
Hypoxia is a serious disease that results from hypoxemia.
What happens if your oxygen level falls to 60?
An extremely low oxygen level is indicated by an ABG test with a PaO2 reading of 60 mmHg or less.
You will almost certainly require supplemental oxygen treatment if your blood oxygen level is that low.
Supplemental oxygen therapy is a therapy that provides you with supplemental oxygen to breathe.
You may normally get additional oxygen through a cannula (tube) that is attached to the exterior of your nose, or you can use a breathing mask.
The oxygen might be delivered directly into your trachea via a tube at times (windpipe).
The manner and amount of time you receive supplemental oxygen therapy depends on your specific requirements. You may also require hospitalization.
What happens if the oxygen falls to 40?
If your blood oxygen level falls below an average of 40 mm Hg, you may experience serious health complications, including hypoxemia (low blood oxygen levels).
Some people even become unconscious at this stage.
Heart failure can also occur in some cases when the oxygen levels drop this low.
Supplemental oxygen therapy is essential at this point to prevent any further health complications from arising.
How do doctors determine if a patient has hypoxemia?
Your doctor will conduct a physical examination to listen to your heart and lungs in order to diagnose hypoxemia. A decrease in blood oxygen may be revealed by abnormalities in these organs.
Your dermatologist may also examine your skin, lips, or fingernails for blue color.
Examinations of your oxygen levels are conducted by doctors, including:
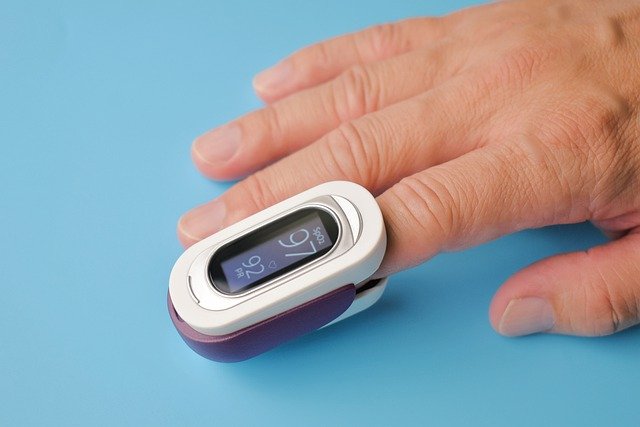
- A sensor that fits over your finger measures the amount of oxygen in your blood. Pulse oximetry is both painless and non-invasive. It’s used by many doctors on a regular basis when you visit.
- The arterial blood gas test is a laboratory procedure that measures the amount of oxygen in your blood.
- These tests can include breathing through tubes connected to computers or other equipment.
How to treat hypoxemia?
Treatment for hypoxemia is aimed at increasing the amount of oxygen in the blood. Physicians can use medications to treat underlying diseases that cause hypoxemia.
These medicines are often delivered as inhalers, which enable you to breathe the medicine directly into your lungs.
Oxygen therapy is also used in extreme cases.
In this case, your doctor may prescribe oxygen therapy. Extra oxygen is provided through a cannula (tube) that is attached to the outside of the nose, or through a breathing mask.
The amount and duration of oxygen treatment are determined on an individual basis. You can receive oxygen at home, while sleeping, or during your everyday activities.
Monitoring and managing hypoxemia
Temporary physical or environmental circumstances can cause low oxygen levels in your blood on occasion.
When this happens, it is rarely dangerous to your health.
In most cases, your blood oxygen levels will return to normal in a matter of hours, and no monitoring or treatment is required.
However, if hypoxemia is caused by a persistent illness, you will almost certainly need to keep monitoring your oxygen levels on a regular basis.
It’s especially critical that you take care of your chronic condition in this situation.
What are the potential problems or negative effects of hypoxemia?
If your blood does not have enough oxygen, it cannot supply the organs and tissues that require it with adequate amounts of oxygen.
If left untreated for a long period of time, this condition may be deadly in the short term, but it can also damage the heart or brain if it persists over time.
This is why you should never ignore symptoms of hypoxemia.
A lack of oxygen can also harm your brain cells by causing them to be damaged or destroyed.
When that happens, they do not heal or grow back. This process leads to the degeneration of the brain over time, which, in turn, leads to memory loss and even Alzheimer’s disease—although this process can take decades to manifest.
- See also: What happens if a particle goes faster than light
- See also: What would happen if the sun approaches earth
Is it possible to avoid hypoxemia?
There are things you may do to avoid hypoxemia from returning after treatment.
Your doctor may advise increasing the amount of oxygen in your blood using one or more of the following methods:
- Breathing exercises
- Walking or yoga are examples of mild exercises.
- Eating a healthy diet, this diet should include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Quitting smoking. Nicotine narrows the blood vessels, which makes it more difficult for your body to get the oxygen it needs.
- Reducing stress levels. When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones that can interfere with how well your
What is the prognosis for individuals who are hypoxemic?
Hypoxemia can be treated, and its symptoms usually go away.
People who suffer from hypoxemia may require therapy on an occasional or continuous basis depending on the underlying cause.
Your doctor will work with you to manage the condition in order for you to live a full, active life.
There are many treatments available to you, but it’s important that you manage your condition responsibly.
If you don’t take care of yourself by taking your medications and following your doctor’s directions for cautiously using oxygen therapy, hypoxemia can come back—and when it does, it may be more serious than the last time.
Conclusion
Hypoxemia is a condition that occurs when the level of oxygen in your blood falls below normal.
This can be caused by an underlying disease, such as emphysema, or a temporary physical or environmental circumstance. Left untreated, hypoxemia can damage the heart or brain over time.
However, it is treatable and most symptoms go away with treatment.