Epilepsy affects millions of people worldwide, causing recurrent seizures that can significantly impact quality of life.
Traditional methods of diagnosing and treating epilepsy have advanced, but there’s a cutting-edge technology making a profound difference: brain mapping.
This innovative technique helps pinpoint the exact areas of the brain responsible for seizures, paving the way for more effective treatments.
In this blog post, we’ll explore what brain mapping is, how it helps with epilepsy, the techniques involved, associated risks, and the future of this promising field.
What is Brain Mapping?
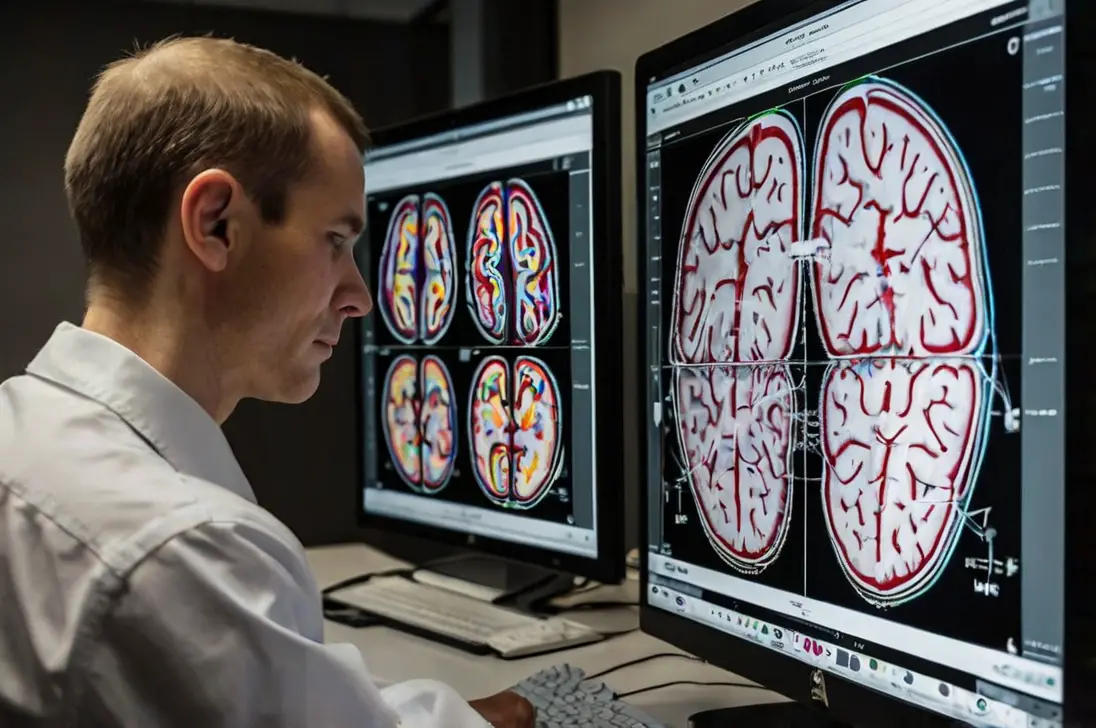
Brain mapping involves using advanced imaging technology to create detailed maps of the brain’s structure and function.
These maps can identify areas responsible for various activities, thoughts, and feelings.
For people with epilepsy, brain mapping can locate the precise regions where seizures originate, which is crucial for diagnosis and treatment.
Brain mapping techniques include functional MRI (fMRI), magnetoencephalography (MEG), and electrocorticography (ECoG).
These methods offer a detailed view of the brain’s activity, helping doctors understand how different regions interact during a seizure.

- Read also: Brain Mapping for Stroke: A Way for Diagnosis and Treatment
- Read also: Organic Brain Damage: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
How Can Brain Mapping Help with Epilepsy?
Brain mapping is a powerful tool that plays a crucial role in managing and treating epilepsy.
Here’s how it can help:
Accurate diagnosis
Brain mapping allows doctors to identify the exact location in the brain where seizures are occurring.
This precise information helps doctors diagnose the type of epilepsy more accurately.
Knowing the specific area affected by seizures is essential because different types of epilepsy require different treatments.
With this detailed information, doctors can create treatment plans that are more effective for each patient.
Surgical planning
For some patients, medications may not be enough to control their seizures, making surgery a viable option.
Brain mapping provides detailed insights into which areas of the brain are involved in seizure activity.
This is critical for surgical planning because it helps surgeons determine which parts of the brain can be safely operated on.
The goal is to address the problem areas without harming regions that control essential functions like speech, movement, or memory.
With brain mapping, surgeons can plan the surgery to maximize success and minimize risks.
Monitoring treatment
Brain mapping is also valuable for monitoring the effectiveness of treatments over time.
Whether a patient is on medication or has undergone surgery, brain mapping can track changes in brain activity.
This helps doctors understand how well the treatment is working and make necessary adjustments.
For example, if brain mapping shows a reduction in seizure activity after starting a new medication, doctors can be confident in continuing that treatment.
If there’s no improvement, they know it’s time to consider other options.

Techniques Used in Brain Mapping
Brain mapping uses several techniques to gain detailed insights into brain function.
Each method has its unique benefits and applications, especially in managing epilepsy.
Functional MRI (fMRI)
Functional MRI (fMRI) is a popular, non-invasive technique that measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow.
When a part of the brain is more active, it receives more blood flow, and fMRI can capture these changes with high-resolution images.
How it works
- During an fMRI scan, patients are asked to perform specific tasks, such as moving a hand or thinking about a word.
- The scanner tracks blood flow to different parts of the brain, helping to identify which areas are involved in these tasks.
Why it’s useful
- fMRI helps doctors understand which parts of the brain control various functions.
- It provides detailed images without the need for surgery or other invasive procedures.
- In epilepsy patients, fMRI can identify areas involved in seizure activity, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a technique that records the magnetic fields produced by neural activity in the brain.
It offers excellent temporal resolution, meaning it can capture rapid changes in brain activity, which is crucial for understanding the dynamics of seizures.
How it works
- During a MEG scan, sensors detect the magnetic fields generated by neurons when they communicate.
- The data is used to create a map of brain activity, showing where and when different brain functions occur.
Why it’s useful
- MEG can pinpoint the exact origin of seizure activity, which is vital for treatment.
- It provides real-time information about brain activity, making it easier to understand how seizures start and spread.
- MEG is non-invasive and can be used repeatedly without risk to the patient.
Electrocorticography (ECoG)
Electrocorticography (ECoG) is an invasive technique that involves placing electrodes directly on the surface of the brain to record electrical activity.
This method provides highly detailed information and is often used during epilepsy surgery.
How it works
- Electrodes are surgically placed on the brain’s surface, allowing for precise measurement of electrical activity.
- ECoG can detect abnormal brain activity that might not be visible with other methods.
Why it’s useful
- ECoG provides the most detailed information about where seizures originate, making it invaluable for surgical planning.
- During epilepsy surgery, ECoG helps guide the surgeon in removing the areas responsible for seizures while preserving critical brain functions.
- Although invasive, ECoG is highly accurate and is often used when other methods do not provide enough detail.

Risks and Precautions
Brain mapping techniques offer important insights into brain function but involve considerations for safety and patient comfort:
Invasiveness
Some brain mapping techniques, like Electrocorticography (ECoG), require surgery to place electrodes directly on the brain’s surface.
This surgery carries risks such as infection, bleeding, and potential damage to surrounding brain tissue.
Neurosurgeons carefully plan these procedures to minimize risks and ensure patient safety.
Exposure to radiation
Certain imaging techniques, such as CT scans used in parts of brain mapping, involve exposure to radiation.
While modern equipment limits radiation exposure, repeated scans over time can potentially pose risks, especially for sensitive individuals.
Doctors carefully assess these risks and opt for alternative techniques when possible.
Discomfort and anxiety
Non-invasive techniques like Functional MRI (fMRI) and Magnetoencephalography (MEG) may cause discomfort or anxiety in patients.
MRI machines are noisy, and patients must stay still in a tight space during the scan.
Medical staff prepare patients for these aspects and provide support to minimize any discomfort or anxiety during the procedure.
Precautions taken
To reduce these risks, medical professionals take several precautions:
- Thorough evaluations: Before brain mapping procedures, patients undergo comprehensive evaluations to assess their overall health.
- Monitoring and support: Patients are closely monitored during and after procedures for any signs of complications.
- Patient education: Patients receive detailed information about what to expect during brain mapping procedures, including potential discomforts, etc.
- Choosing safest options: Doctors prioritize using non-invasive techniques or alternatives whenever feasible, especially for patients who may be more vulnerable to complications.

The Future of Brain Mapping for Epilepsy
The future of using brain mapping to treat epilepsy is looking bright, with ongoing advancements focused on making treatments more accurate, less invasive, and better for patients.
Here’s what’s on the horizon:
Machine learning and AI
Researchers are exploring how to use machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) alongside brain mapping data.
This means computers can analyze large amounts of brain scan information to predict when seizures might happen more accurately.
AI can also help doctors choose the best treatments, like medicines or surgeries, based on what each patient needs.
Non-invasive techniques
There’s a lot of effort going into developing ways to get detailed brain information without invasive methods, like putting electrodes on the brain.
New imaging technologies and techniques are making it possible to see the brain’s activity clearly without needing surgery.
This helps reduce risks and discomfort for people with epilepsy.
Personalized medicine
Brain mapping improvements are leading to more personalized treatment plans for epilepsy patients.
By understanding how each person’s brain works in detail, doctors can customize treatments more precisely.
This makes sure treatments work well and have fewer side effects by targeting the exact parts of the brain causing seizures.

- Read also: Head Over Heels: Recognizing a Brain Bleed After a Fall
- Read also: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Transverse Cerebral Fissure
Conclusion
Brain mapping represents a significant leap forward in the diagnosis and treatment of epilepsy.
By providing detailed maps of brain activity, this technology helps doctors make more accurate diagnoses, plan safer surgeries, and monitor treatment effectiveness.
While there are risks associated with some techniques, ongoing research and technological advancements promise a future where brain mapping is even more effective and accessible.
For those living with epilepsy, brain mapping offers hope for better management and improved quality of life.