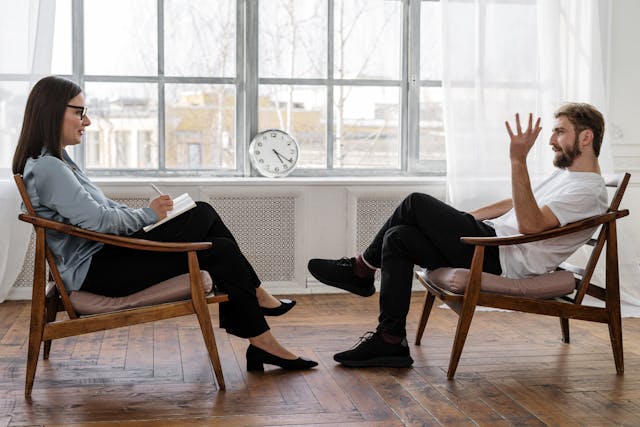
Mental health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being, and seeking help from a therapist can be a vital step towards improving your mental health.
However, with various therapeutic approaches available, it can be challenging to determine which one is right for you.
In this blog post, we will discuss the key differences between positive psychology and traditional therapy, helping you understand which approach may be more suitable for your needs.
What is Positive Psychology?
Positive psychology is a field within psychology dedicated to exploring the positive aspects of human life. Its focus extends to elements like happiness, well-being, and personal growth.
The core idea is to highlight and cultivate positive emotions, relationships, and experiences to contribute to an individual’s overall sense of well-being.
In the realm of positive psychology, practitioners employ Positive Psychology Interventions (PPIs), strategies crafted to foster positive emotions, enhance personal strengths, and ultimately improve an individual’s overall state of well-being.
Key Principles of Positive Psychology
Positive Psychology, with its focus on enhancing well-being, is grounded in several key principles that contribute to a fulfilling and positive life:
Gratitude
Gratitude involves actively recognizing and appreciating the positive aspects of life, no matter how small.
By fostering a habit of gratitude, individuals can experience improvements in psychological well-being, reduced stress levels, and even enhanced physical health.
It’s a powerful practice that encourages a positive perspective.
Optimism
Optimism is an outlook that leans towards viewing challenges and opportunities through a positive lens.
It involves expecting successful outcomes, even in the face of difficulties or uncertainties.
Embracing optimism is linked to better mental and physical health outcomes, as well as increased resilience when confronted with life’s challenges.
Resilience
Resilience is the ability to adapt and bounce back from adversity.
Positive psychology encourages individuals to cultivate resilience by focusing on their strengths and developing effective coping skills.
This principle underscores the importance of learning and growing from life’s setbacks.
Mindfulness
Mindfulness is the practice of being fully present and engaged in the current moment.
This involves paying attention to thoughts and feelings without judgment.
Mindfulness has proven benefits, including improvements in mood, stress reduction, and overall enhanced well-being.
It encourages individuals to savor and appreciate each moment.
PERMA Model
The PERMA model, devised by Martin Seligman, provides a comprehensive framework for understanding well-being. It consists of five essential elements:
- Positive emotions: Embracing positive emotions and learning to enjoy oneself in the present moment.
- Engagement: Becoming fully absorbed in activities that one enjoys and excels at, fostering a state of flow and fulfillment.
- Relationships: Cultivating deep and meaningful connections with others, recognizing the significance of social bonds in promoting well-being.
- Meaning: Dedication to a cause or something larger than oneself, finding purpose and significance in life.
- Accomplishment/Achievement: Thriving through setting and achieving goals, contributing to a sense of fulfillment and accomplishment.

What is Traditional Therapy?
Traditional therapy, often referred to as psychotherapy, represents a conventional method of mental health treatment.
It centers on tackling negative emotions, thoughts, and behaviors to assist individuals in coping with mental health challenges like anxiety, depression, and trauma.
The approaches within traditional therapy encompass a range of methodologies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), psychodynamic therapy, and interpersonal therapy.
This form of therapy is grounded in addressing and understanding the root causes of mental health issues to promote healing and improved well-being.
Key Principles of Traditional Therapy
Traditional therapy encompasses several key principles that guide its approach to mental health and well-being:
Client-centered
Traditional therapy places a strong emphasis on the client’s unique perspective and experiences.
This client-centered approach underscores the importance of being true to oneself to lead a fulfilling life.
The therapist works collaboratively with the client, acknowledging their autonomy and individuality.
Exploration of past experiences
A fundamental aspect of traditional therapy involves delving into a person’s past experiences to uncover the root causes of current issues.
This exploration often includes examining childhood experiences, past traumas, or significant past relationships.
By understanding the influence of the past, individuals can gain insight into present challenges.
Relationship building
Building a strong therapeutic relationship is a cornerstone of traditional therapy.
Therapists create a non-judgmental and empathetic environment, fostering open and honest communication.
This relationship serves as a foundation for trust and collaboration, essential for effective therapy.
Technique integration
Traditional therapists adopt a flexible approach by integrating various therapeutic techniques based on the client’s needs.
These techniques may include cognitive-behavioral methods, mindfulness practices, or expressive arts therapy.
The integration of diverse methods allows therapists to tailor their approach to the unique requirements of each individual.
Psychodynamic approach
Traditional therapy often incorporates a psychodynamic approach, focusing on unconscious processes influencing a person’s present behavior.
This approach aims to enhance client self-awareness and understanding of the impact of the past on the present.
Exploring unconscious elements contributes to a deeper understanding of thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.

Traditional vs. Positive: Key Differences
| Aspect | Traditional Approach |
Positive Approach
|
| Problem-Solving Focus | Focuses on identifying and fixing problems or shortcomings. |
Emphasizes building on strengths and finding constructive solutions.
|
| Feedback Style | Tends to be critical and highlights what is wrong or lacking. |
Emphasizes constructive feedback, reinforcing positive behaviors.
|
| Mindset Orientation | Often rooted in a fixed mindset, resisting change or adaptation. |
Fosters a growth mindset, embracing change and continuous improvement.
|
| Communication Style | Can be authoritative or directive, emphasizing rules and control. |
Encourages open communication, collaboration, and shared decision-making.
|
| Goal Setting Approach | Goals may be rigidly defined and focused on avoiding failure. |
Encourages flexible goals with an emphasis on personal and collective growth.
|
| Approach to Challenges | Tends to view challenges as obstacles or threats to be overcome. |
Views challenges as opportunities for learning, growth, and innovation.
|
| Employee Motivation | May rely on external motivators, such as fear of consequences. |
Focuses on intrinsic motivation, encouraging a sense of purpose and autonomy.
|
| Team Dynamics | Hierarchical structures with a clear chain of command. |
Encourages collaborative and inclusive team dynamics.
|
| Change Management Approach | Change may be resisted or implemented with resistance. |
Embraces change as a natural part of growth and development, fostering adaptability.
|
Finding the Right Approach for You
Finding the right approach for your mental health needs depends on various factors, such as your personal preferences, the nature of your mental health concerns, and the therapeutic approach that resonates with you.
Here are some steps to help you determine the best approach for you:
Self-assessment
Reflect on your personal preferences and what you are looking for in a therapeutic approach.
Consider factors such as the type of support you need, your comfort level with discussing past experiences, and your willingness to engage in various therapeutic techniques.
Research
Learn about the key principles of positive psychology and traditional therapy.
Understand the benefits and limitations of each approach, and consider how they align with your personal preferences and needs.
Consult a mental health professional
Discuss your concerns and preferences with a mental health professional.
They can provide guidance on which approach may be more suitable for your needs and help you determine the best course of action for your mental health.
Trial and error
It may take some time to find the right approach that works for you.
Be open to trying different therapeutic techniques and be willing to adjust your approach if needed.
Patience and persistence
Remember that mental health treatment is a process, and it may take time to see progress.
Stay patient and persistent in your search for the right approach, and be willing to adjust your expectations and goals as needed.

Conclusion
Both positive psychology and traditional therapy have their unique benefits and can be effective in promoting mental health and well-being.
Understanding the key differences between these approaches can help you make an informed decision on which approach is best suited for your needs.
Remember, it is essential to discuss your concerns with a mental health professional to determine the most appropriate therapeutic approach for your unique situation.
FAQs
Positive psychology focuses on cultivating positive emotions, relationships, and experiences, while traditional therapy focuses on addressing negative emotions, thoughts, and behaviors.
While positive psychology is primarily focused on enhancing overall well-being, it can also be used in conjunction with traditional therapy to address specific mental health concerns.
Discuss your needs and preferences with a mental health professional to determine the best approach for your individual situation.