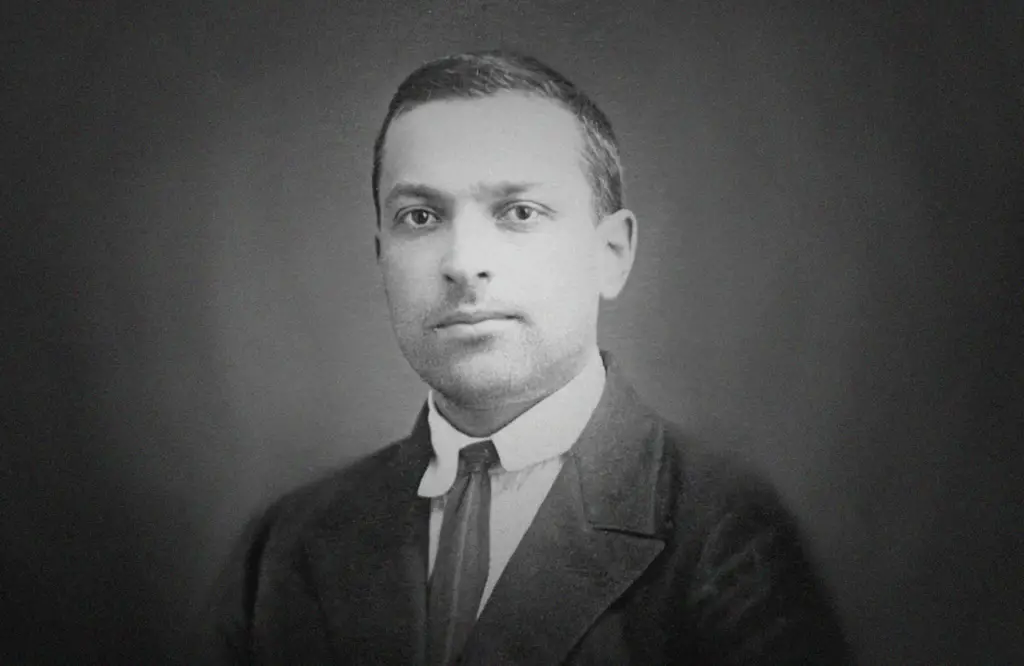
Lev Vygotsky, a Russian psychologist, revolutionized the field of developmental psychology with his theory of social development.
Unlike other theories that emphasized individual learning, Vygotsky’s theory placed social interaction at the core of cognitive development.
He believed that learning is inherently a social process, deeply influenced by culture, language, and interaction with others.
In this blog post, we will delve into the key concepts of Vygotsky’s theory, explore its implications for education, and discuss its relevance in today’s world.
Key Concepts of Vygotsky’s Theory
Vygotsky’s theory is built on several foundational concepts that explain how children develop cognitively through social interaction.
Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD)
The Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) is one of Vygotsky’s most significant contributions.
ZPD refers to the range of tasks that a child can perform with the help of a more knowledgeable other (MKO) but cannot yet accomplish independently.
The ZPD is the gap between what a child can do on their own and what they can achieve with guidance.
This concept emphasizes the importance of social interaction in learning, suggesting that children learn best when they are challenged just beyond their current abilities, with support from someone more experienced.
- Read also: Emotional Development Stages: Everything You Need to Know
- Read also: From Puberty to Adulthood: Adolescent Development Stages
Scaffolding
Scaffolding is closely related to the ZPD.
It refers to the temporary support provided by an MKO, such as a teacher, parent, or peer, to help the child accomplish a task within their ZPD.
As the child’s competence increases, the scaffolding is gradually removed, allowing the child to take on more responsibility until they can perform the task independently.
This process highlights the dynamic nature of learning and the crucial role of social interaction in cognitive development.
Language and thought
Vygotsky also emphasized the interconnection between language and thought.
He argued that language is a fundamental tool for cognitive development because it enables communication, social interaction, and the internalization of knowledge.
According to Vygotsky, children initially use language for social purposes, such as interacting with others, but over time, it becomes internalized as inner speech, guiding their thoughts and actions.
This progression from external to internal language is essential for the development of higher cognitive functions.

Implications of Vygotsky’s Theory for Education
Vygotsky’s theory has profound implications for educational practices, particularly in how teaching and learning are approached.
Collaborative learning
Collaborative learning, where students work together to solve problems or complete tasks, is a key application of Vygotsky’s theory.
Since Vygotsky believed that social interaction is crucial for cognitive development, collaborative learning allows students to learn from each other within their ZPDs.
By engaging in discussions, sharing ideas, and working together, students can extend their understanding and achieve more than they could alone.
Research supports the effectiveness of collaborative learning, showing that it can lead to deeper understanding and better retention of information.
Teacher as a guide
In a Vygotskian classroom, the teacher’s role shifts from being the sole provider of knowledge to being a guide or facilitator.
Teachers should focus on identifying each student’s ZPD and providing the appropriate level of support or scaffolding to help them progress.
This approach requires teachers to be attuned to the individual needs of their students and to create opportunities for meaningful social interaction in the classroom.
By guiding students through their ZPDs, teachers can foster independent learning and critical thinking skills.
Assessment
Vygotsky’s theory also suggests a shift in how student progress is assessed.
Traditional assessments often focus on what a student can do independently, but Vygotsky’s approach emphasizes the importance of assessing a student’s potential for learning with guidance.
Dynamic assessment, which evaluates a student’s ability to learn with support, aligns with this perspective.
This type of assessment provides a more comprehensive understanding of a student’s capabilities and can inform more personalized and effective teaching strategies.

Vygotsky’s Theory in the Modern World
Vygotsky’s theory remains highly relevant in today’s educational landscape and beyond.
As our understanding of learning and development evolves, Vygotsky’s emphasis on social interaction, culture, and language continues to influence modern educational practices.
Technology and online learning
In the digital age, Vygotsky’s ideas about social learning have found new applications in online and technology-enhanced learning environments.
Collaborative tools like discussion forums, social media, and virtual classrooms facilitate social interaction, allowing learners to engage with peers and instructors from around the world.
These platforms can create virtual ZPDs where students learn from each other and receive guidance in real-time, much like in a traditional classroom setting.
Cultural sensitivity in education
Vygotsky also stressed the role of culture in cognitive development, arguing that learning is deeply influenced by the cultural context in which it occurs.
In today’s increasingly diverse and globalized world, this aspect of Vygotsky’s theory underscores the importance of culturally responsive teaching.
Educators are encouraged to recognize and incorporate students’ cultural backgrounds into the learning process, making education more relevant and effective.

- Read also: The Power of Perception: Key Concepts in Social Psychology
- Read also: Influential Figures: Exploring 5 Key Figures in Social Psychology
Conclusion
Vygotsky’s theory of social development offers a powerful framework for understanding how children learn and develop cognitively.
By emphasizing the importance of social interaction, language, and culture, Vygotsky’s ideas challenge us to rethink traditional approaches to education and assessment.
His concepts, such as the Zone of Proximal Development and scaffolding, have had a lasting impact on educational practices and continue to shape how we approach teaching and learning in the modern world.
As we continue to explore the complexities of human development, Vygotsky’s work remains a vital reference point for educators, psychologists, and researchers alike.