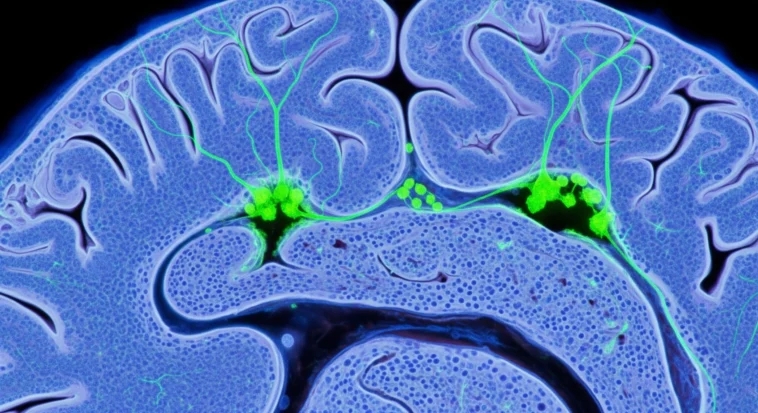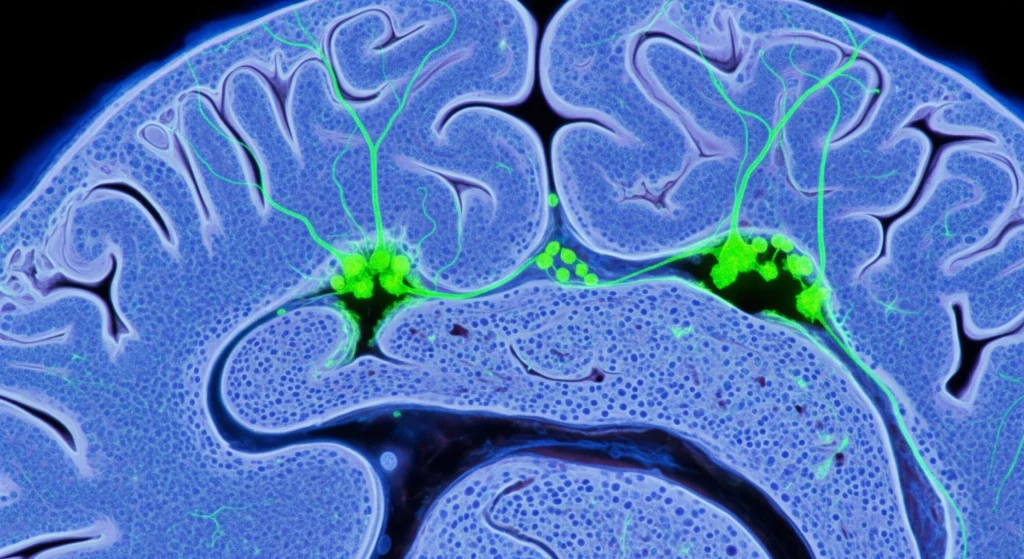
For a long time, scientists said the adult brain was a finished product — no new neurons, no surprises.
Picture someone telling you your brain is like an old phone that never gets updates.
Sounds bleak, right? Thankfully that’s not true.
Turns out your brain can still grow new neurons in adulthood through a process called adult neurogenesis.
Tiny stem cells awaken, go through careful stages, and become fully working neurons that plug into existing circuits — kind of like a skilled construction crew adding new rooms and wiring them into an old house.
What Is Adult Neurogenesis?
Adult neurogenesis is just a fancy way of saying your brain can still make new neurons, even after you’re “grown up.”
Think of it like upgrading your gaming console without buying a whole new system — your brain adds new parts to improve performance.
Back in the day, scientists thought this only happened when your brain was first developing, like building the foundation of a house.
But now we know certain brain areas keep producing fresh neurons that slip right into old circuits, like new players joining an experienced team.
This process helps your brain repair, adapt, and even get sharper over time. Pretty wild, right?
The Primary Neurogenic Niches in Adult Brains
Your brain doesn’t just pop out new neurons everywhere — it has special “hotspots” called neurogenic niches where the magic happens.
Think of them as secret workshops hidden inside your brain.
The dentate gyrus of the hippocampus
This spot is like your brain’s memory upgrade center.
It helps you tell similar experiences apart — like remembering the difference between where you parked your bike today versus yesterday.
Here, new neurons are born from special stem-cell-like helpers and wired into your memory circuits.
The subventricular zone
This area cranks out neurons that travel along a “neural highway” to the olfactory bulb, where your sense of smell gets fine-tuned.
In humans, though, this smell-based neurogenesis isn’t as strong, but it still gives us clues about how adaptable the brain can be.
The Five Critical Stages of Adult Neurogenesis
So here’s the wild part: turning a quiet little stem cell into a fully functioning brain cell isn’t instant magic — it’s more like a five-level quest.
Each stage has its own rules, checkpoints, and challenges, kind of like leveling up in a video game.
Let’s walk through it.
Stage 1: Neural stem cell activation
Imagine a bunch of stem cells just chilling, half-asleep, waiting for a signal to wake up.
These guys are like teammates sitting on the bench until the coach (your environment) calls them in.
Exercise, learning something new, or even hanging out with friends can send the “wake up” signal.
Once they’re activated, they start dividing — the first domino in the neurogenesis chain reaction.
Stage 2: Proliferation and expansion
Now the action ramps up. Those stem cells start multiplying like crazy, turning into a growing army of new recruits.
But here’s the catch — the brain has to balance making enough new cells without draining the stem cell pool.
Think of it like managing your savings account: you want growth, but you can’t blow through the whole stash at once.
Stage 3: Neuroblast formation and early differentiation
Here’s the point of no return. Some of those cells commit to becoming neurons — no take-backs.
They transform into neuroblasts, which are like rookie brain cells getting their uniforms on.
They’re not fully trained yet, but they’ve picked their career path.
Stage 4: Migration and positioning
This is where it gets epic.
These baby neurons have to travel across dense, busy brain neighborhoods without wrecking the place.
Picture moving through a packed concert crowd while carrying something fragile — you’ve got to squeeze through, follow signals, and end up in the exact right spot.
The brain uses chemical signposts and guide ropes to help them get there.
Stage 5: Differentiation, maturation, and integration
Finally, the neuroblasts settle down and grow into fully functional neurons.
They sprout dendrites (the “listening” branches) and axons (the “talking” wires).
Then comes the hardest part: making friends.
New neurons have to plug into existing brain circuits, form connections, and actually prove they’re useful.
Some connections strengthen, others get pruned, until everything clicks.
Factors Influencing Adult Neurogenesis
Your brain’s ability to make new neurons isn’t fixed — it dances with a bunch of ups and downs depending on what you do and what happens to you.
Some things fan the flames and help new neurons survive; others put them out.
Here’s the lowdown, straight-up and real.
Promoting Factors
- Physical exercise: Regular aerobic exercise boosts molecules like BDNF which help stem cells wake up and newborn neurons survive.
- Learning and enrichment: Challenge your brain, learn a song, pick up coding, try a new language, and your brain rewards you by making and fitting in new neurons.
- Adequate sleep: While you snooze, your brain clears waste, balances hormones, and tunes growth signals so new neurons can thrive.
Inhibiting Factors
- Chronic stress: Long-term stress floods your system with cortisol and other nasty signals that shut down stem cell growth and kill off newbies.
- Aging: As we get older, the pool of active stem cells and the brain’s efficiency in making new neurons tend to drop.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation creates a toxic neighborhood for growing neurons. It’s like trying to plant a garden in polluted soil — growth gets hard.
Clinical Implications and Therapeutic Potential
Understanding how adult neurogenesis works isn’t just some cool trivia — it could literally change how we treat brain disorders.
Depression, anxiety, Alzheimer’s… a lot of these conditions tie back to problems with how new neurons are born and wired in.
Depression and mood disorders
Ever notice how when you’re really down, it feels like your brain is stuck in a loop?
That might actually be because your neuron-making system is running low.
Fun fact: many antidepressants don’t just tweak chemicals — they seem to boost neurogenesis, helping the brain grow fresh neurons that plug into mood circuits.
Think of it like updating your playlist when you’re sick of the same sad songs — suddenly, there’s new rhythm and variety.
Cognitive enhancement
New neurons in the hippocampus are like memory ninjas.
They help you separate similar experiences — like remembering today’s math class notes versus yesterday’s.
If scientists figure out how to safely crank up neurogenesis, it could help people struggling with memory loss or give older brains a sharper edge.
Imagine your grandma suddenly crushing you at memory games — that’s the dream.
Neuroprotection and recovery
Here’s the real superhero angle: if we can boost neurogenesis, we might help the brain repair itself after injury or fight back against diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
It’s like having a built-in repair crew, patching up circuits and replacing what’s been lost.
Not perfect yet, but the potential is jaw-dropping.
Current Research Frontiers and Future Directions
Neuroscientists aren’t done — they’re just getting started.
To truly crack the code of adult neurogenesis, they’re diving deeper into how stem cells tick at every stage of their journey.
And the tools they’re using? Next-level.
Multi-omics approaches
Think of this as checking a cell’s diary, playlist, and secret code all at once.
By studying RNA, proteins, and epigenetic “switches,” researchers can see exactly what gears are turning inside a newborn neuron.
Single-cell technologies
Instead of looking at the crowd, scientists now zoom in on individuals.
They can track single cells through their entire life cycle and have already found that not all stem cells are the same — some are like sprinters, others like marathon runners.
Translational research
Animal studies give us the blueprint, but the big challenge is figuring out how much of this applies to humans.
Scientists are now bridging that gap, asking: how much neuron-making power do our adult brains really have?
Controversies and Ongoing Debates
Here’s the plot twist: not everyone agrees on how much neurogenesis really happens in adult humans.
Some studies say it slows down big time after childhood, while others insist we keep making fresh neurons throughout life.
A big snag? Even in animal studies, scientists argue about when a mouse or rat officially counts as “adult.”
And since those timelines matter for comparing results, it’s like trying to debate teenage vs. adult rules without agreeing on the age cutoff.
Practical Applications and Lifestyle Implications
Here’s the cool part: all this brain science isn’t just for labs — it actually matters for your life.
Knowing what helps or hurts neurogenesis means you can take charge of your brain’s health, almost like leveling up your own neural superpowers.
Exercise? Total brain booster. A run, a dance battle, or even shooting hoops tells your neurons, “Wake up, time to grow!”
Learning? Every new skill — whether it’s guitar chords, coding, or even TikTok edits — pushes your brain to build fresh connections.
Stress? Yeah, too much of it is like a weed killer for new neurons. That’s why managing it — through hobbies, talking it out, or just chilling — matters.
And don’t underestimate sleep. Your brain uses it to clean house and prep the ground for new growth.
On the flip side, chronic stress, bad sleep habits, and overdoing things like alcohol are like throwing roadblocks in front of your brain’s renewal crew.
Conclusion
Adult neurogenesis flips the old idea of the brain being “fixed” on its head.
From sleepy stem cells waking up to brand-new neurons wiring into your circuits, your brain is always finding ways to renew itself.
The more we learn, the closer we get to using this natural repair system to fight depression, memory loss, or even brain injuries.
And here’s the hopeful part: your choices matter. Exercise, learning, sleep, and managing stress are like fuel for this renewal engine.