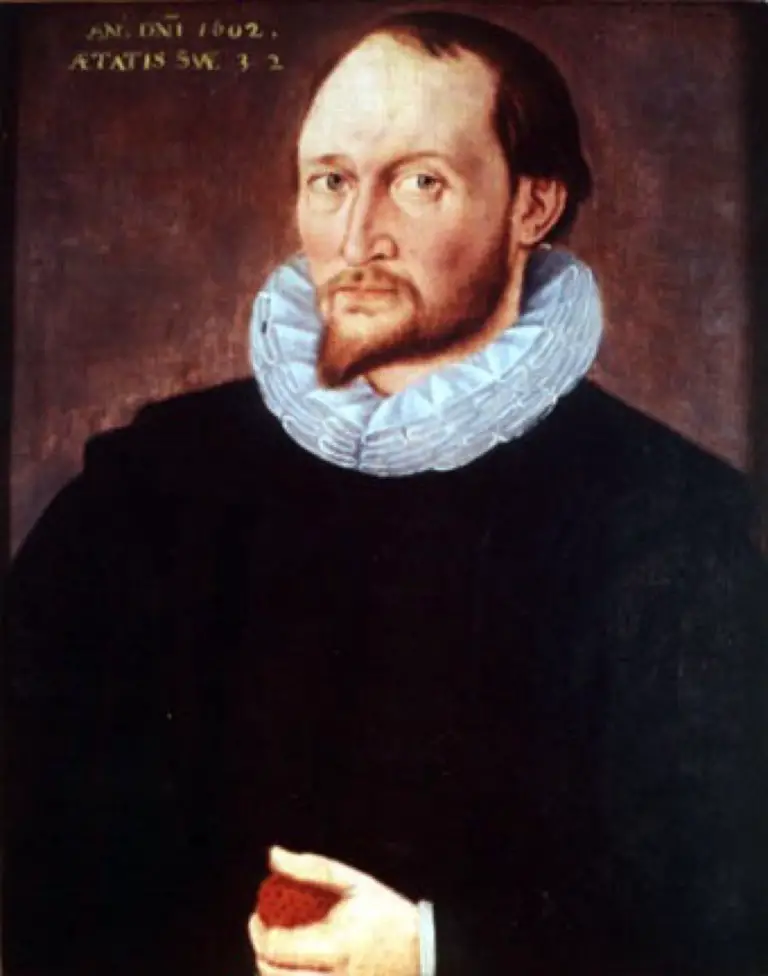
Thomas Harriot was a renowned Renaissance scientist who made significant contributions to various fields, including astronomy, mathematics, optics, meteorology, and ethnography.
Born in 1560 in London, England, Harriot’s life and early influences played a crucial role in shaping his scientific pursuits.
In this blog post, we will delve into Harriot’s life, his scientific contributions, and his lasting legacy.
Harriot’s Life and Early Influences
Thomas Harriot, an English mathematician, received his education at Oxford University.
During his formative years, he was notably influenced by his association with Sir Walter Raleigh, a prominent entrepreneur and statesman of the time.
Harriot’s connection with Raleigh led to his role as Raleigh’s navigational advisor, where he contributed significantly to Raleigh’s endeavors to establish a trading colony in the Americas.
This early collaboration with Raleigh not only shaped Harriot’s professional trajectory but also provided him with valuable real-world experience in navigation and exploration.
- Read also: The Renaissance Era’s Impact on Science Advancements
- Read also: History of Science and Technology
Harriot’s Scientific Contributions
Astronomy
Harriot’s pioneering work in astronomy earned him recognition as one of the foremost scientists of his time.
He was among the first to utilize a telescope for astronomical observations, predating the famous observations made by Galileo Galilei.
Harriot’s keen observations led to groundbreaking discoveries, including the first recorded observations of sunspots and the discovery of Jupiter’s moons.
These discoveries revolutionized our understanding of the solar system and laid the foundation for future astronomical research.
Mathematics
Harriot’s contributions to mathematics were equally profound.
He played a key role in the development of algebra, making significant advancements in the field.
One of his most notable achievements was the independent discovery of logarithms, a fundamental concept in mathematics.
Harriot’s innovative approach to mathematics, demonstrated through the use of geometric and algebraic methods, paved the way for the development of calculus and other advanced mathematical theories.
Other Scientific Pursuits
Beyond his influential work in astronomy and mathematics, Thomas Harriot made significant strides in several other scientific fields:
Optics
Harriot’s investigations into optics focused on understanding how light behaves and interacts with different materials.
Through experiments and observations, he uncovered fundamental principles that laid the groundwork for advancements in optical science.
Harriot’s research contributed to the development of optical instruments, such as lenses and telescopes, which have since become indispensable tools in scientific exploration and everyday life.
Meteorology
Driven by his curiosity about the natural world, Harriot delved into the study of meteorology, aiming to unravel the mysteries of weather patterns and atmospheric phenomena.
His meticulous observations and analyses of weather conditions helped expand our understanding of meteorological processes and their impact on the environment.
Harriot’s insights into meteorology have proven invaluable for predicting weather patterns, mitigating natural disasters, and informing agricultural practices.
Ethnography
During his expeditions to the Americas, Harriot embarked on a journey of cultural exploration, documenting the customs, traditions, and ways of life of indigenous peoples.
His studies in ethnography provided valuable insights into the diverse cultures and societies encountered during his travels.
By recording detailed observations and interactions with indigenous communities, Harriot contributed to the broader field of ethnography, enriching our understanding of human diversity and cultural heritage.
Harriot’s Legacy
Thomas Harriot’s legacy in the field of science is profound, despite the fact that he did not publish his findings while he was alive.
Instead, his groundbreaking work was meticulously recorded in manuscripts, which were later unearthed and examined by scholars.
Harriot’s contributions spanned various areas, including the development of the Harriotian telescope, the study of logarithms, and the documentation of the Algonquian culture.
Harriot’s legacy lives on through his pioneering efforts in scientific exploration and discovery.
His development of the Harriotian telescope laid the groundwork for advancements in astronomical observation, while his independent discovery of logarithms contributed to the advancement of mathematics.
- Read also: Who Invented Math? The History of Essential Knowledge in Sciences
- Read also: Who Invented Eyeglasses? The History Behind Proper Eye Care
Conclusion
Thomas Harriot was a remarkable Renaissance scientist who made significant contributions to various fields of study.
His life and early influences played a crucial role in shaping his scientific pursuits, and his work laid the groundwork for future advancements in mathematics, astronomy, and other scientific disciplines.
Despite not publishing his findings during his lifetime, Harriot’s legacy continues to inspire and inform scientific research today.