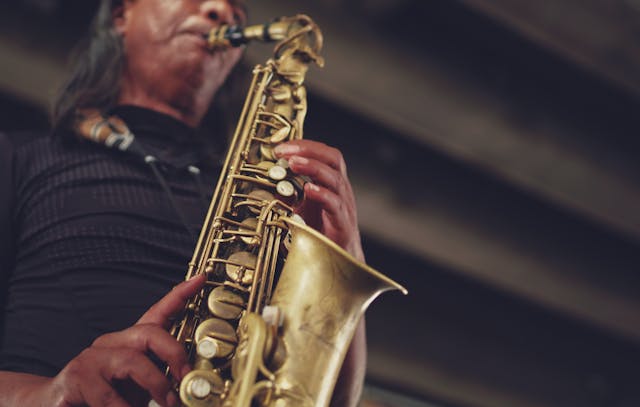
Renaissance music, spanning from the 14th to the 16th centuries, is characterized by its polyphonic structure and the use of various instruments.
This period marked a significant shift in music composition, with a focus on harmony, counterpoint, and melody.
In this blog post, we will explore the characteristics of Renaissance music, the development of harmony, and the instruments and composers of this time.
Characteristics of Renaissance Music
Characteristics of Renaissance music reflect the artistic and cultural advancements of the period.
Here’s a deeper look into the defining features:
- Read also: Famous Renaissance Poets Who Shaped Literature
- Read also: Famous Harlem Renaissance Poets
Polyphony
Polyphony, or the interweaving of multiple independent melodies, was a hallmark of Renaissance music.
Composers skillfully crafted intricate compositions where each voice contributed to the overall harmonic texture.
This intricate layering of melodies added depth and complexity to the music, distinguishing it from the monophonic texture of earlier eras.
Vocal vs. instrumental music
Renaissance music encompassed both vocal and instrumental compositions.
Vocal music, performed by choirs or soloists, was prevalent in both sacred and secular contexts.
It adorned religious ceremonies, such as Masses and motets, while also gracing courtly gatherings and private concerts.
Instrumental music, on the other hand, flourished in secular settings, providing entertainment for social events, dances, and festivities.
Secular vs. sacred music
Renaissance composers produced a rich repertoire of both secular and sacred music.
Secular music, intended for non-religious purposes, reflected the joys and sorrows of everyday life.
Madrigals, chansons, and dances delighted listeners with their colorful melodies and expressive lyrics.
In contrast, sacred music served the spiritual needs of the church, comprising Masses, motets, and hymns that conveyed reverence and devotion through solemn melodies and intricate harmonies.
Development of harmony
The Renaissance witnessed significant advancements in harmonic techniques.
Composers explored the nuances of harmony, moving beyond the modal system of the Middle Ages to embrace more complex chordal structures and polyphonic textures.
Experimentation with consonance, dissonance, and counterpoint gave rise to a rich harmonic palette, enhancing the emotional depth and expressive range of Renaissance music.

The Instruments of the Renaissance
During the Renaissance period, a diverse array of musical instruments enriched the soundscape of the era’s compositions:
Stringed instruments
Lutes and viols were prominent stringed instruments known for their gentle, melodious tones.
These instruments were favored for their versatility and ability to evoke a sense of intimacy in performances.
Wind instruments
Flutes, recorders, and shawms added vibrant and lively timbres to Renaissance music.
Their bright, resonant sounds contributed to the dynamic and spirited nature of the compositions.
Keyboard instruments
Harpsichords and organs were pivotal keyboard instruments that offered a wide range of tonal possibilities.
They provided a foundation for harmonic accompaniment and allowed for the exploration of diverse musical textures and colors.
Vocal ensembles
Renaissance vocal ensembles were celebrated for their clarity and expressiveness.
Emphasizing polyphony and counterpoint, these ensembles delivered intricate and harmonically rich performances.
They frequently graced the sacred settings of churches and cathedrals, enhancing religious services with their divine melodies.

Famous Composers of the Renaissance
The Renaissance era boasts a plethora of renowned composers whose contributions have left an enduring impact on the history of music.
Here are some of the most notable figures:
Giovanni Palestrina
Giovanni Palestrina is celebrated for his refined and elegant polyphonic compositions, which epitomize the Renaissance ideal of sacred music.
His works, characterized by their intricate counterpoint and expressive harmonies, continue to be revered for their beauty and spirituality.
William Byrd
William Byrd, a prolific English composer, made significant contributions to both secular and sacred music.
His compositions spanned a wide range of genres, including motets, madrigals, and keyboard music.
Byrd’s mastery of harmony and melodic invention established him as one of the foremost composers of the Renaissance period.
Claudio Monteverdi
Claudio Monteverdi is hailed as a pioneer in the development of opera and the advancement of expressive vocal techniques.
His innovative approach to music challenged conventional norms, leading to the emergence of the Baroque style.
Monteverdi’s operatic masterpieces, such as “L’Orfeo” and “The Coronation of Poppea,” remain iconic landmarks in the history of Western music.
Josquin des Prez
Josquin des Prez, often referred to as the “master of the notes,” was renowned for his impeccable craftsmanship and profound musical expression.
His compositions, characterized by their intricate counterpoint and lyrical beauty, exerted a profound influence on subsequent generations of composers.
Josquin’s works continue to be studied and admired for their timeless elegance and emotional depth.
Thomas Morley
Thomas Morley was a versatile composer and theorist whose contributions enriched both secular and sacred music.
He is best known for his madrigals, which exemplify the vibrant and expressive style of Elizabethan music.
Morley’s theoretical writings also played a significant role in shaping the musical practices of his time.
Orlando di Lasso
Orlando di Lasso, also known as Roland de Lassus, was a prolific composer whose works encompassed a wide range of genres, including choral music, madrigals, and sacred motets.
His mastery of polyphony and rich harmonic language earned him widespread acclaim across Europe.
Lasso’s compositions reflect a profound understanding of the human voice and its expressive capabilities.

- Read also: Things To Know: Harlem Renaissance Literature Facts
- Read also: Facts About The Harlem Renaissance
Conclusion
The Renaissance era marked a period of creativity and exploration in music, characterized by a keen interest in polyphony, harmony, and instrumental diversity.
Visionary composers like Giovanni Palestrina and William Byrd played pivotal roles in shaping the evolution of music during this time, leaving a lasting legacy of artistic innovation and advancement.